Refer to
Front and Rear Ignition Control Modules
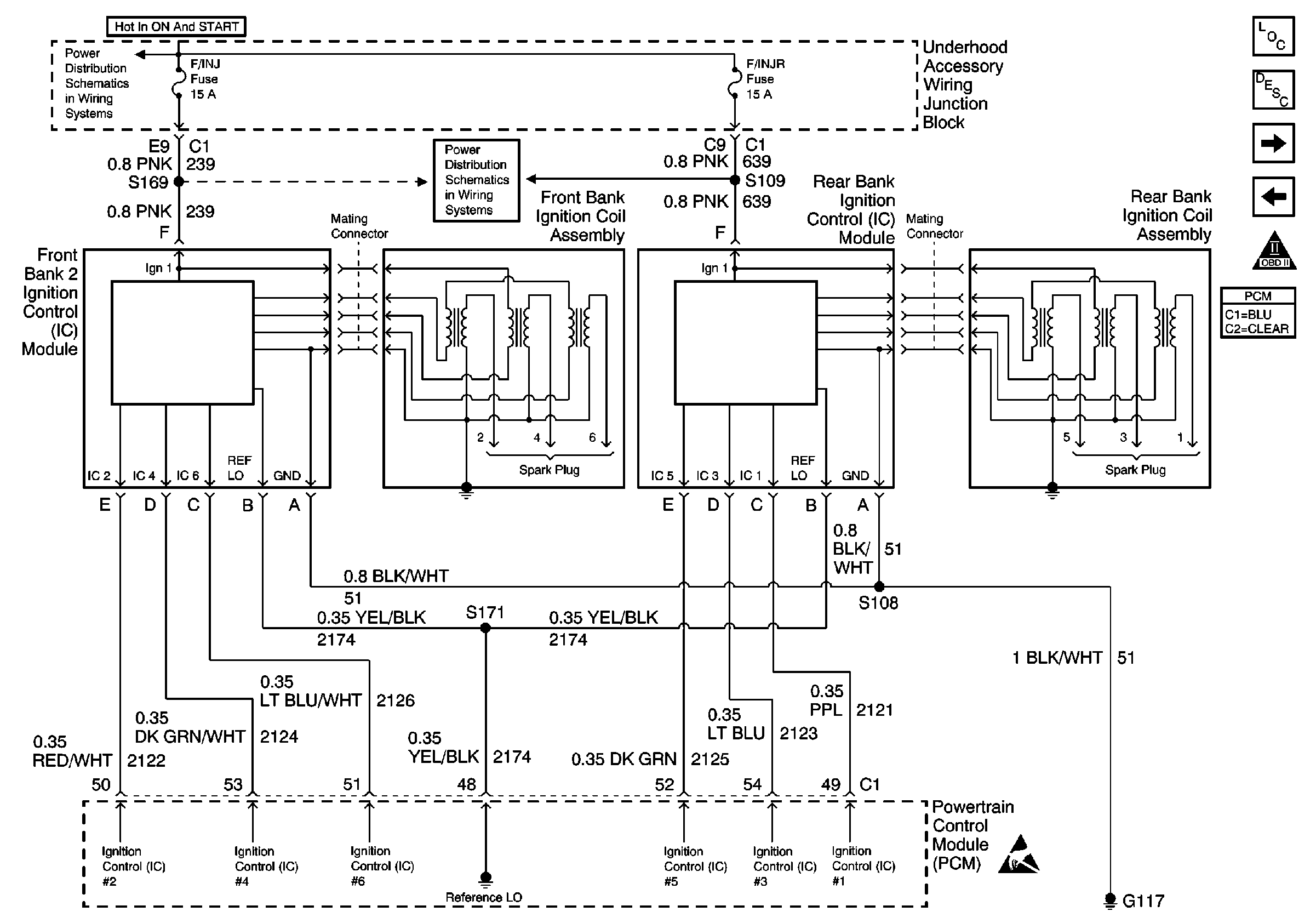
in Engine Controls Schematics
.
Circuit Description
The ignition system on this engine uses an individual ignition coil for each cylinder. An ignition coil assembly consisting of three coils and an ignition control module (ICM), is located in the center of each cam cover. This arrangement allows the ignition coil to connect directly to the spark plug using only a boot. This eliminates the need for secondary ignition wires. There are separate ignition modules for bank 1 and for bank 2. Each module controls the three ignition coils for that bank of cylinders. The powertrain control module (PCM) controls ignition module operation. There are six ignition control (IC) circuits, one per cylinder, that connect the PCM and the ignition modules. The ignition modules also have a power feed, a chassis ground circuit, and a reference low circuit each. The PCM causes spark to occur by pulsing the IC circuit, which signals the ignition module to trigger the ignition coil and fire the spark plug. Sequencing and timing are PCM controlled.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition voltage is between 9.0-17.0 volts. |
| • | The conditions are met for less than 1.0 second. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects an incorrect voltage potential on the ignition control circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
With no fault detected, the scan tool will display OK continuously. If a fault is detected, the display may fluctuate between OK and Fault, or display Fault continuously. If Fault is displayed, even momentarily, this should be considered fault present.
-
Refer to the system mechanization for the fuses which supply these circuits.
Step
| Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool continuously indicate OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 | Is an entire bank of cylinders inoperative? | -- | ||
Are the ignition system fuses OK? | -- | |||
5 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||
6 | Connect a test lamp between the ignition feed circuit and the ground circuit in the ignition control module harness. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||
7 | Using the DMM, measure the resistance between the ground circuit and the reference low circuit in the ignition control module harness connector. Is the resistance less than or equal to the specified value? | 5 ohms | ||
8 |
Important: Remove the fuel pump fuse before proceeding. Running or cranking the engine with an ignition control module disconnected will cause excessive engine fueling if the fuel pump is not disabled.
Is the frequency within the specified range? | 2-20 Hz | ||
9 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 1.0 V | ||
10 |
Is the resistance less than or equal to the specified value? | 5 ohms | ||
11 | Using the DMM, check for continuity between the ignition control circuit and ground. Is continuity indicated? | -- | ||
12 | Check for a short to ground in the ignition control module ignition feed circuit. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
13 | Repair the open ignition control module ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Repair open ignition control module ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 | Repair the open or high resistance ignition control module reference low circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Repair the open or high resistance in the ignition control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
17 | Repair the ignition control circuit shorted to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
18 | Repair the ignition control circuit shorted to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
19 |
Is continuity indicated? | -- | ||
20 | Repair the ignition control circuits that are shorted together. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
21 | Check for poor connections and terminal tension at the ignition control module harness connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
22 |
Do the LEDs flash for all three cylinders? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
23 | Replace the ignition control module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
24 | Check for poor connections and terminal tension at the PCM harness connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Was a problem found and corrected. | -- | ||
25 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
26 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
27 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
