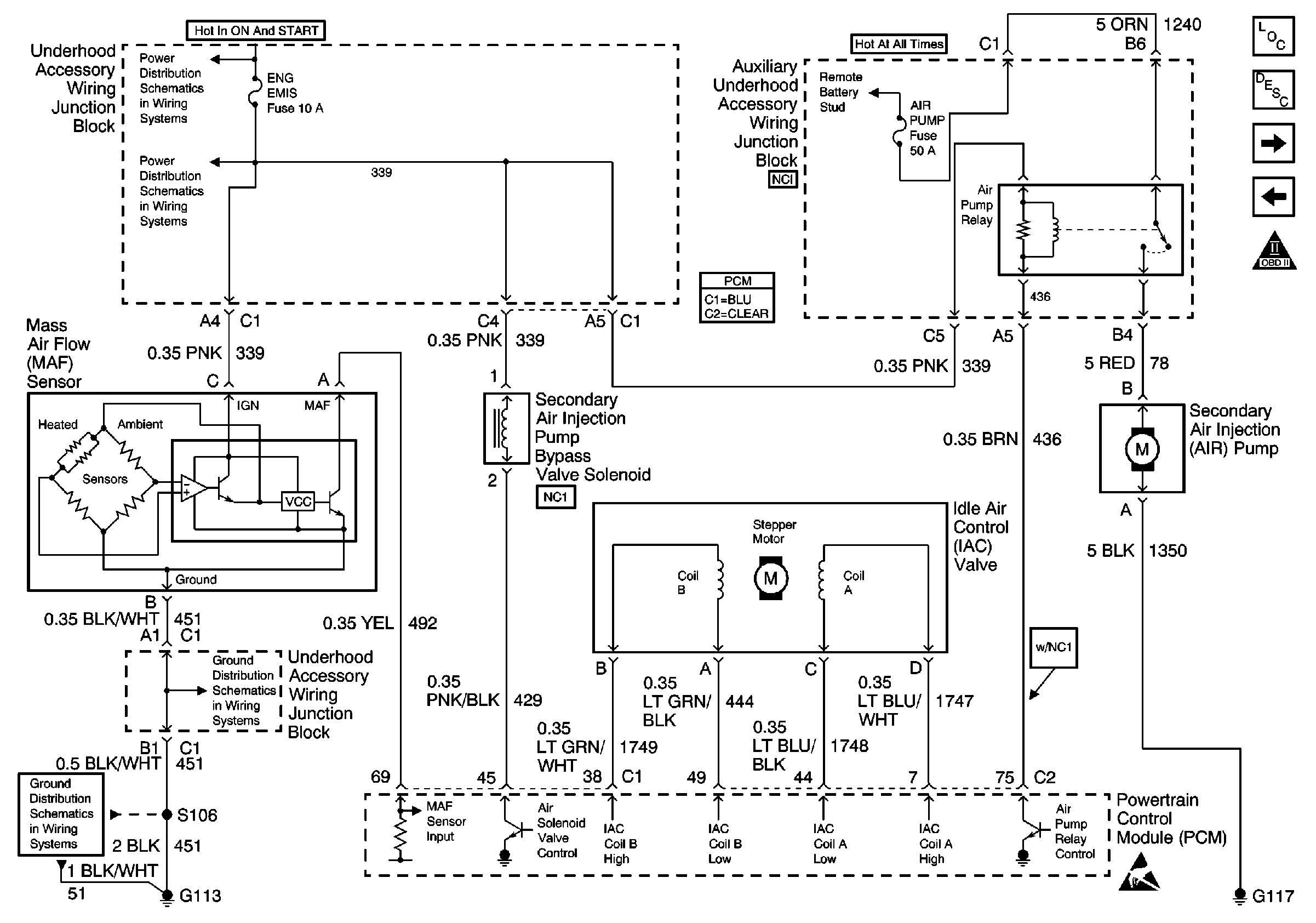
Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
MAF, Secondary Air Injection Pump Bypass Solenoid, IAC and Secondary
AIR Pump
.
Circuit Description
The AIR pump is used on this vehicle to lower tail pipe emissions on start-up. The powertrain control module (PCM) grounds the AIR pump relay control circuit, which energizes the AIR pump. The PCM also grounds the AIR solenoid valve control circuit, which energizes the AIR solenoid valve. The AIR solenoid valve opens allowing manifold vacuum to open the AIR control valves. The PCM enables both control circuits when AIR system operation is desired. When the AIR system is active, the AIR pump forces fresh air into the exhaust stream in order to accelerate catalyst operation. The AIR control valves replace the conventional check valves. When the AIR system is inactive, the AIR control valves prevent air flow in either direction. DTC P0412 applies to the AIR solenoid control circuit. DTC P0418 applies to the AIR pump relay control circuit. DTC P0410 sets if an air flow problem is detected.
The PCM will run two tests using the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) voltage to diagnose the AIR system. Both tests have two parts.
The passive test is performed during regular AIR pump operation. The passive test consists of the following:
Passive Test Part 1
When the AIR system is enabled, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. If the HO2S voltage goes below a threshold, the PCM interprets this as an indication that the AIR system is operational.
Passive Test Part 2
When the AIR system is disabled, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. The HO2S voltage should increase above a threshold and switch normally.
If both of these tests indicate a pass, no further action is taken. If one of the above tests failed or is inconclusive, the diagnostic will proceed to test two.
The active test is performed specifically for diagnostic purposes. Test two consists of the following:
Active Test Part 1
During this test the PCM turns the AIR system on during closed loop operation. When the AIR system is activated, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. If the AIR system is operating properly, the HO2S voltage should go below a predetermined threshold.
Active Test Part 2
The PCM turns the AIR system off. The HO2S voltage should return to above a rich threshold.
The PCM will repeat test two up to 4 consecutive times with a short delay between each command.
If the PCM determines that the HO2S voltage did not respond as expected during the tests, DTC P0410 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0101, P0102, P0103, P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0300, P0412, P0418, P0442, P0443, P1441 and HO2S DTCs not set. |
| • | The engine operates for more than 3 seconds. |
Test 1
| • | The engine speed is more than 400 RPM |
| • | The engine load is less than 80 percent. |
| • | The engine air flow is less than 35 g/s. |
| • | The ignition voltage is more than 11.5 volts. |
| • | The air fuel ratio is more than 13:1. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is less than 40°C (104°F). |
| • | The entake air temperature (IAT) is more than 10°C (50°F). |
| • | The power enrichment, dDeceleration fuel cut off, or catalyst over temperature not active. |
| • | The AIR system is enabled for 50 seconds. On a hot start, the AIR system operation will be delayed for 60 seconds after start-up. |
| • | Test 1 fails if: |
| • | HO2S voltage does not go below 300 mV for 25 seconds during pump operation. |
| • | HO2S voltage does not go above 600 mV during the 15 seconds after the pump is turned off. |
Test 2
| • | The engine operates for more than 5 minutes. |
| • | The engine speed is more than 400 RPM. |
| • | The EVAP purge is active |
| • | The maximum air flow is 35 g/s. |
| • | The ECT is more than 10°C (50°F). |
| • | The ignition voltage is more than 11.5 volts. |
| • | The engine load is less than 80 percent. |
| • | The fuel system is operating in closed loop. |
| • | Test 2 fails if the HO2S voltage is above 300 mV for 4 seconds during pump operation. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
If the HO2S voltage does not behave as expected during either of the tests, a failure is reported.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Notice: Do not operate the AIR pump for more than 60 seconds. Continuous operation of the AIR pump in excess of 60 seconds will damage the AIR pump.
Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can aid in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also aid in determining how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same Freeze Frame conditions, such as RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc., that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
DTC P0412 AIR Solenoid Valve Control Circuit and P0418 AIR Pump Relay Control Circuit should be diagnosed first if either are set.
-
The AIR pump is not designed to run continuously. If the pump needs to be replaced, check for conditions that may cause continuous pump operation.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Are DTCs P0412 or P0418 set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | ||
3 | Is the fuse that supplies power to the AIR pump OK? | -- | ||
4 | Turn the AIR pump ON and OFF using a scan tool. Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF? | -- | ||
5 | Is the AIR pump running continuously? | -- | ||
6 |
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||
7 | Jumper the B+ supply circuit to the AIR pump feed circuit using a fused jumper wire. Does the AIR pump operate? | -- | ||
8 |
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||
9 | Connect a test lamp between the two terminals on the harness side in the AIR pump electrical connector. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||
10 |
Is air flow present at the AIR pump outlet? | -- | ||
11 |
Is air flow present at both AIR hose and pipe outlets? | -- | ||
12 | With the engine running, check for engine vacuum at the AIR solenoid valve. Is vacuum present at the valve? | -- | ||
13 |
Is vacuum present at both vacuum lines? | -- | ||
14 |
If the solenoid valve is operating properly, vacuum is present at the solenoid valve port when the AIR system is ON, and no vacuum is present when the AIR system is OFF. Is the solenoid valve operating properly? | -- | ||
15 |
Does the fuse open? | -- | ||
16 |
Does the fuse open? | -- | ||
17 |
Does the fuse open? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
18 | Disconnect the AIR pump relay. Is the pump still running? | -- | ||
19 | Repair the open B+ supply circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
20 | Repair the feed circuit to the AIR pump. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
21 | Repair the open or high resistance AIR pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
22 | Repair the short to ground in the ignition feed circuit to the relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
23 | Repair the short to ground in the circuit between the AIR pump relay and the AIR pump. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
24 | Check for a restriction, blockage, disconnect, or other damage to the AIR hoses or pipes between the AIR pump and the AIR solenoid valves. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
25 | Repair the vacuum system as neccessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
26 | Repair the AIR pump feed circuit shorted to power. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
27 | Replace the AIR pump relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
28 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
29 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
30 | Replace the solenoid valve. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
31 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
Replace the AIR pump. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
33 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
34 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
