Special Tools
| • | EN-49077 Compression Pressure Gage
|
Note: Test the compression pressure for each cylinder. The following conditions should be considered when you check the cylinder compression.
| • | The engine should be at normal operating temperature. |
| • | The battery must be at or near full charge. |
| • | The engine cranking time for compression test should be less than 10 seconds at interval of 30 seconds. |
- Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor (CKP) connector.
- Remove the fuel pump relay from the engine room fuse box.
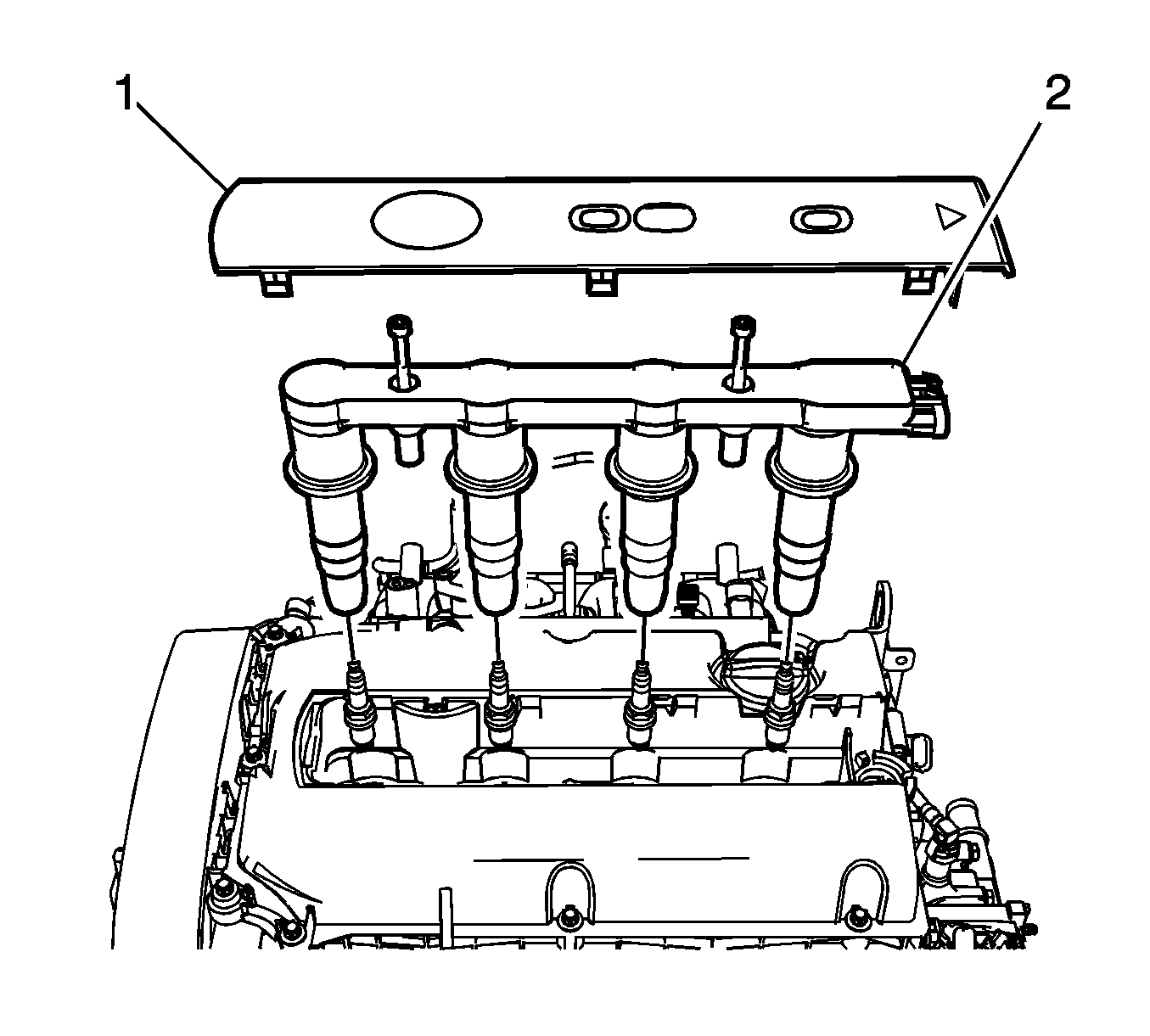
- Remove the ignition coil cover (1).
Caution: Refer to Fastener Caution in the Preface section.
- Remove the ignition coil (2) and spark plugs and tighten.
| • | The ignition coil bolt to 8 N·m (70.8 lb in). |
| • | The spark plug to 25 N·m (18.4 lb ft). |
- Crank the engine with the start motor to remove a foreign substance in the cylinder within 5 seconds.
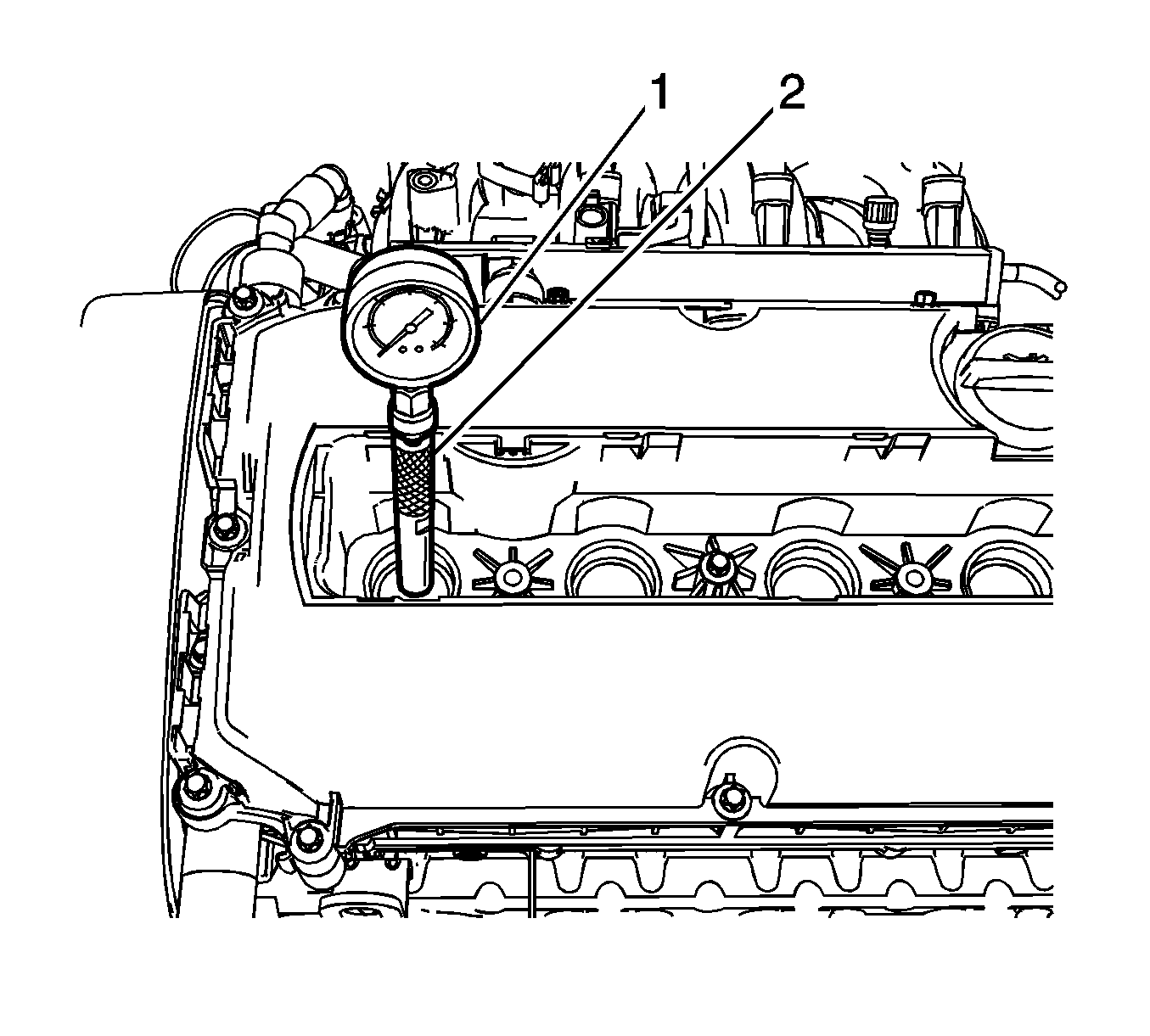
- Install
EN-49077 gage
(1) and
EN-49154 adapter
(2) in the spark plug hole for the cylinder that is being checked.
- Using the vehicles starter motor, rotate or crank the engine for less than 4 seconds at interval of 30 seconds by an assistant.
- Read the compression pressure gage.
- Compare the all cylinder values. Maximum pressure differential 100 kPa (14.50 psi). Engine revs at least 300 RPM.
- Examine the gage readings obtained after the four "puffs" per cylinder are obtained from cranking the starter motor.
The readings are explained in the following descriptions:
| • | Normal Condition: Compression builds up quickly and evenly to the specified compression on each cylinder. |
| • | Piston Rings Faulty: Compression is low on the first stroke and tends to build up on following strokes, but the compression pressure does not reach normal. The compression pressure improves considerably with the addition of oil into the cylinder. |
| • | Valves Faulty: Low compression pressure on the first stroke. The compression pressure does not tend to build up on the following strokes. The compression pressure does not improve much with the addition of oil into the cylinder. |
- Repeat the above procedure in the rest cylinders.


