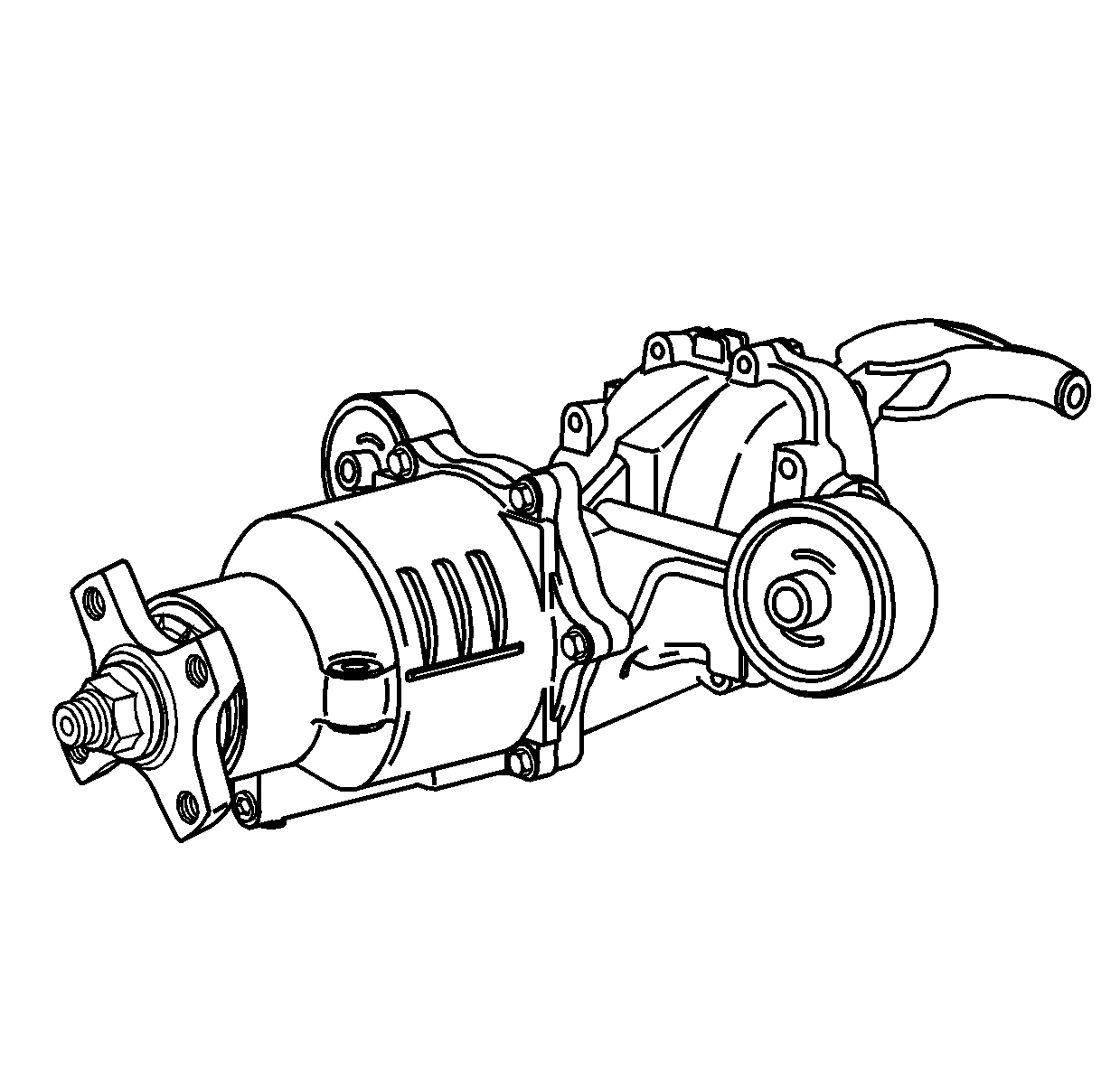
The AWD vehicle is powered by the L61 2.2L 4 cylinder engine. Motion is transferred from the engine crankshaft/flywheel through the M16 CVT automatic transaxle. Or the L81 V6 engine with the M45 5 speed automatic transaxle. A ring and pinion design transfer case is mated to the right side of the transaxle. The transfer case transfers torque/power to the rear differential via a two-piece propeller shaft assembly.
The propeller shaft assembly is of a two-piece design. The front propeller shaft consists of a front plunging type constant velocity joint, a rear universal joint, and a rear yoke . The rear propeller shaft consists of a center bearing assembly, a rear universal joint, and a rear flange. The front propeller shaft yoke, internal splines, is mated to the shaft, external splines, of the rear propeller shaft and is retained by a snap ring. The center bearing assembly provides support and is mounted to the vehicle underbody. The front constant velocity joint and the rear flange are mated to the transfer case and rear axle by reusable bolts and retainers.
The on-demand rear differential distributes variable torque/power to the rear wheels via individual axle shaft assemblies. The rear differential consists of an aluminum housing, a clutch drum/hydraulic pump assembly, and a ring and pinion assembly.
The system operates as follows: On-demand drive is provided to the rear wheels only when slippage is detected at the front wheels. As long as there is no slippage at the front wheels, there is no front-to-rear speed difference and no applicable rear wheel drive torque. There is a small amount of front to rear speed difference built into the system that maintains a small amount of residual torque to the rear wheels. This eliminates clunk on engagement. In the event there is front-to-rear wheel speed difference/slippage, a rotation speed difference between the gerotor pump components, rotor and housing, occurs. In those instances, the rotor draws fluid from the sump and, through the internal passages of the differential housing, sends pressurized fluid to a piston, actuating the rear clutch drum.
