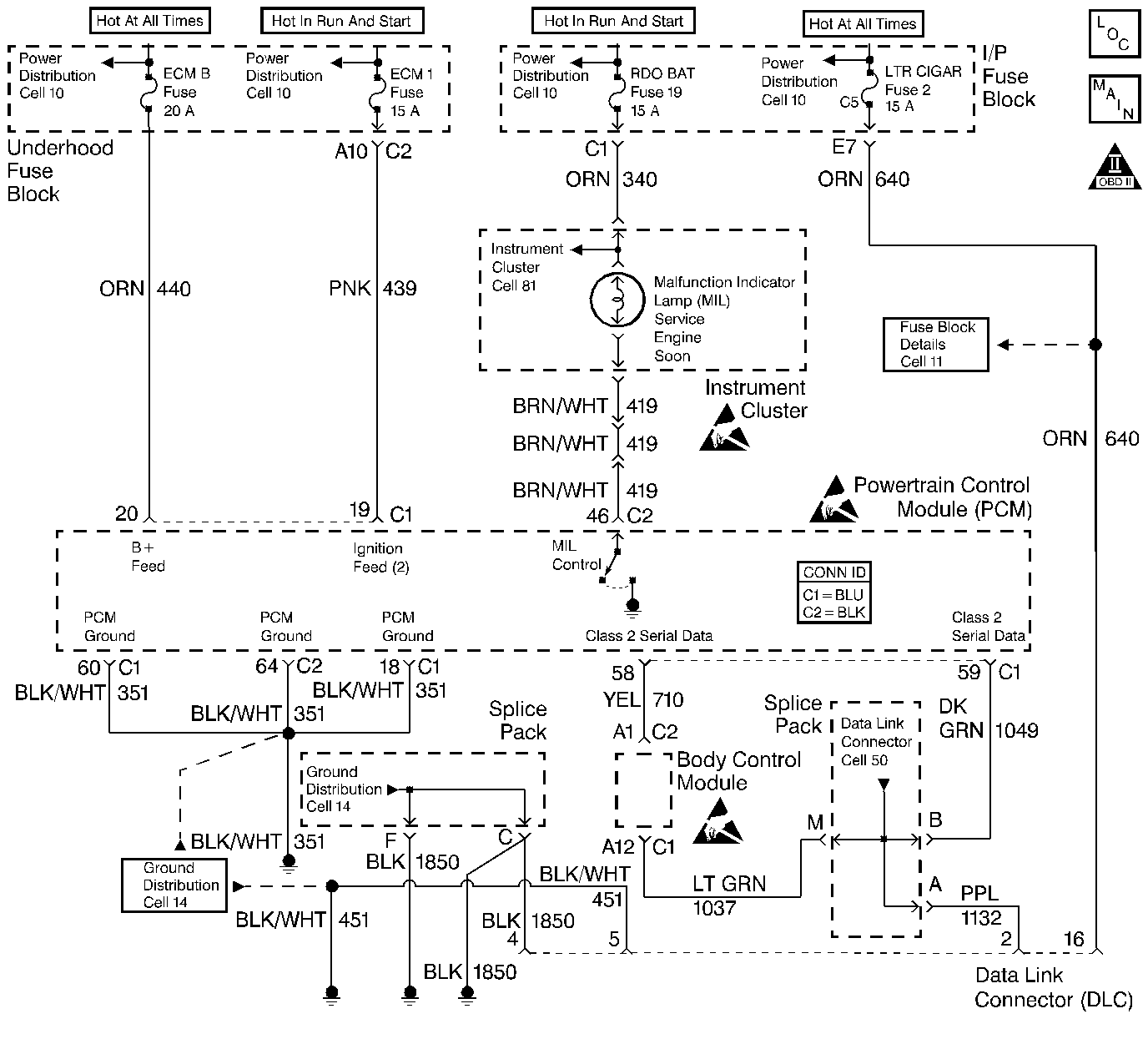
Circuit Description
When the ignition is turned ON, the MIL will momentarily flash ON then OFF then remain ON until the engine is running, if no diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are stored. Battery voltage is supplied through the ignition switch directly to the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) telltale. The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the MIL by providing a ground path through the MIL control circuit in order to turn ON the MIL.
Diagnostic Aids
An open ignition fuse causes the MIL to be inoperative.
Check any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent problem for the following conditions:
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool, if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
Connections that are suspected of being malfunctioning should be thoroughly checked as described in the diagnostic aids.
-
If the engine fails to start and the MIL is inoperative, then the malfunction can be isolated to one of the following items:
-
Probing the MIL circuit with a test light to ground simulates the PCMs control of the MIL. If the MIL illuminates, then the malfunction can be isolated to the control of the MIL or a poor harness connection at the MIL terminal to the PCM. Electrical connections that are suspected of malfunctioning should be thoroughly checked as described in the diagnostic aids.
-
It takes very little resistance for the battery and the ignition 1 feed circuits to cause an intermittent condition. The battery and the ignition 1 feed circuits should also be checked for a poor electrical connection as described in diagnostic aids.
-
Program the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming.
-
A shorted MIL circuit can be diagnosed with a scan tool.
-
An open MIL circuit can be diagnosed with a scan tool. .
-
The PCM grounds will only cause a problem if all of the grounds are not making a good connection. If the PCM ground problem is suspected, the most probable place to check is where all of the grounds meet, at the engine block. Connections that are suspected of malfunctioning should be thoroughly checked as described in the diagnostic aids.
-
If no malfunctions are present at this point and no DTCs were set, refer to the diagnostic aids for additional checks and information.
| • | Open PCM ignition feed 1 circuit |
| • | Open battery feed circuit |
| • | Poor ground at the engine block |
| • | Malfunctioning PCM |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to | ||||||||||
2 | Turn ON the ignition leaving the engine OFF. Is the MIL ON? | -- | ||||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||||
Attempt to start the engine. Does the engine start? | -- | |||||||||||
5 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||||||
7 |
Are the fuses OK? | -- | ||||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||||
9 | Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||
10 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||
11 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
|
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to the Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming .
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
Repair the short to voltage in the MIL control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||||
15 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||
16 | Repair open battery positive voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
17 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||
18 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||
19 | Repair the open in the battery positive voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
20 | Replace the IPC. Refer to Instrument Cluster Replacement in Instrument Panel, Gages and Console. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||||
Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
