Trim Height Measurements
Trim height is a predetermined measurement relating to vehicle ride height. Incorrect trim heights can cause bottoming out over bumps, damage to the suspension components and symptoms similar to wheel alignment problems. Check the trim heights when diagnosing
suspension concerns and before checking the wheel alignment.
Perform the following before measuring the trim heights:
- Make sure the vehicle is on a level surface, such as a alignment rack.
- Remove the alignment rack floating pins.
- Set the tire pressures to the pressure shown on the certification label. Refer to
Vehicle Certification Label
in General Information.
- Check the fuel level. Add additional weight if necessary to simulate a full tank.
- Make sure the rear compartment is empty except for the spare tire.
- Close the doors and hood.
Z Height Measurement
Important: K models only the Z height must be adjusted before the alignment.
The Z height dimension measurement determines the proper ride height for the front end of the vehicle. Vehicles equipped with torsion bars use a adjusting arm in order to adjust the Z height dimension. Vehicles without torsion bars have no adjustment
and could require replacement of suspension components.
Important: All dimensions are measured vertical to the ground. Cross vehicle Z heights should be within 12 mm (0.47 in) to be considered correct.
- Place hand on the front bumper and jounce the front of the vehicle. Make sure that there is at least 38 mm (1.5 in) of movement while jouncing.
- Allow the vehicle to settle into position.
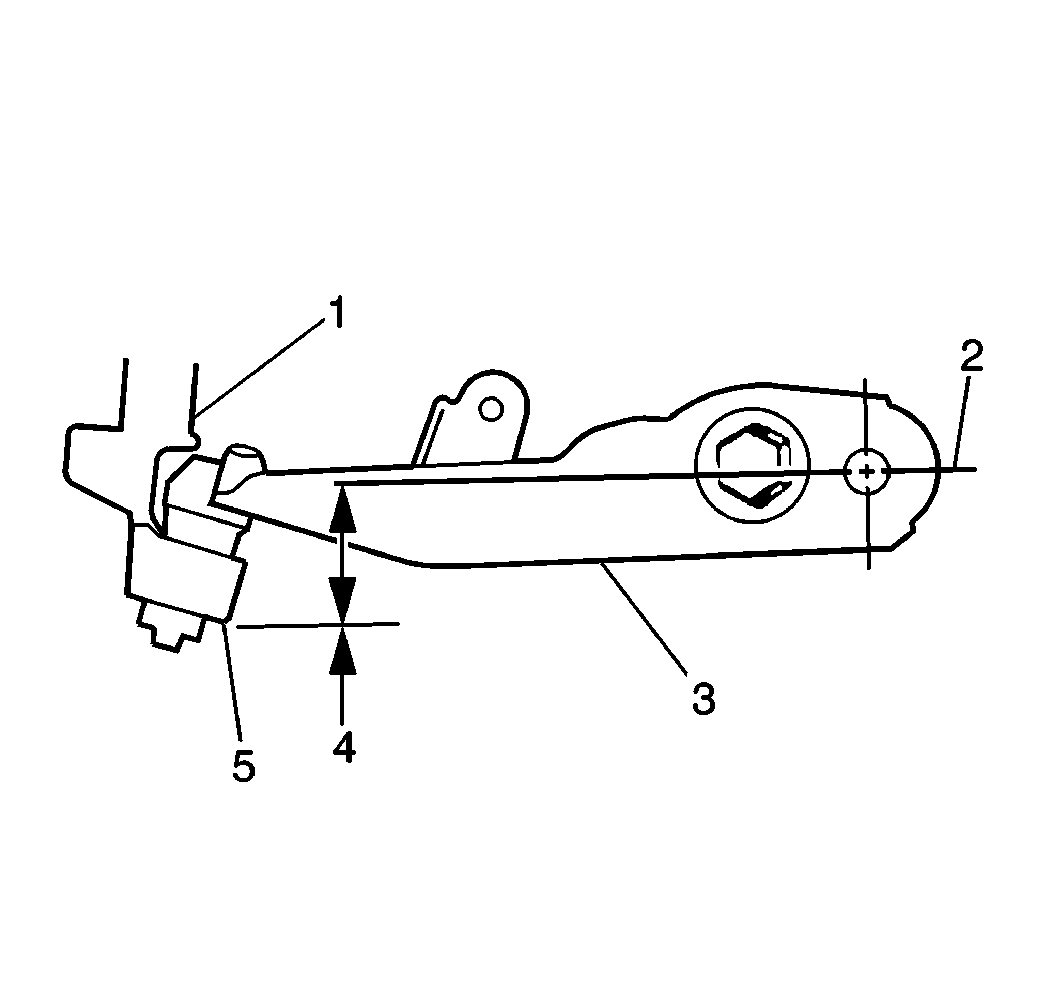
- Measure from the pivot bolt center line (2) down to the lower corner (5) of the steering knuckle (1) in order to obtain the Z height
measurement (4).
- Repeat the jouncing operation 2 more times for a total of 3 times.
- Use the highest and the lowest measurements to calculate the average height.
- The true Z height dimension number is the average of the highest and the lowest measurements. Refer to
Trim Height Specifications
.
Z Height Adjustment
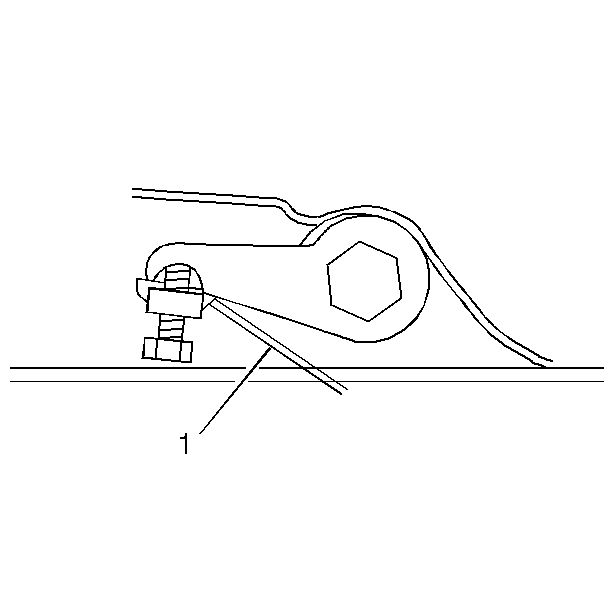
- For vehicles equipped with a torsion bar suspension turn the bolt (1) that contacts the torsion arm clockwise to raise the
and counterclockwise to lower the height adjustment. One revolution of the bolt (1) into the nut increases the Z height by approximately 6.0 mm (0.2 in).
- For vehicles without torsion bars, replace damaged or worn components as necessary.
D Height Measurement
Important: There are no specified trim heights specifications on leaf spring vehicles because it is not an adjustable feature. The height of the suspension will depend on the option content of the vehicle as well as the aftermarket
equipment that is placed on the vehicle. The measurements are used for comparison only and should be within 15 mm with the vehicle at curb and no accessories.
- With the vehicle on a flat surface, lift upward on the rear bumper 38 mm (1.5 in).
- Allow the vehicle to settle into position.
Important: Measure the metal to metal contact points of the rear axle to the frame on the inboard side of the leaf springs.
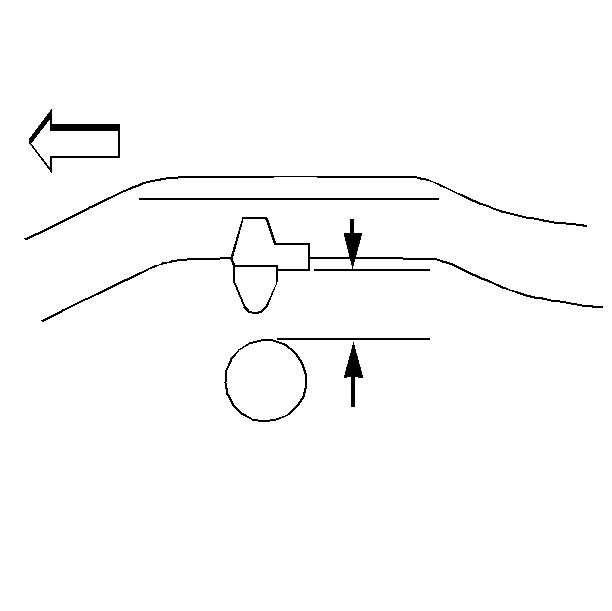
- Measure the D height by measuring the distance between the bumper bracket and the top of the rear axle tube.
- Repeat the jouncing operation 2 more times for a total of 3 times.
- Use the highest and lowest measurements to calculate the average height.
- The true D height dimension number is the average of the highest and the lowest measurements.
- If these measurements are out of specifications, inspect for the following conditions:
| • | Sagging front suspension |
| • | Sagging rear leaf/coil springs |
| • | Improper tire inflation |
| • | Improper weight distribution |



