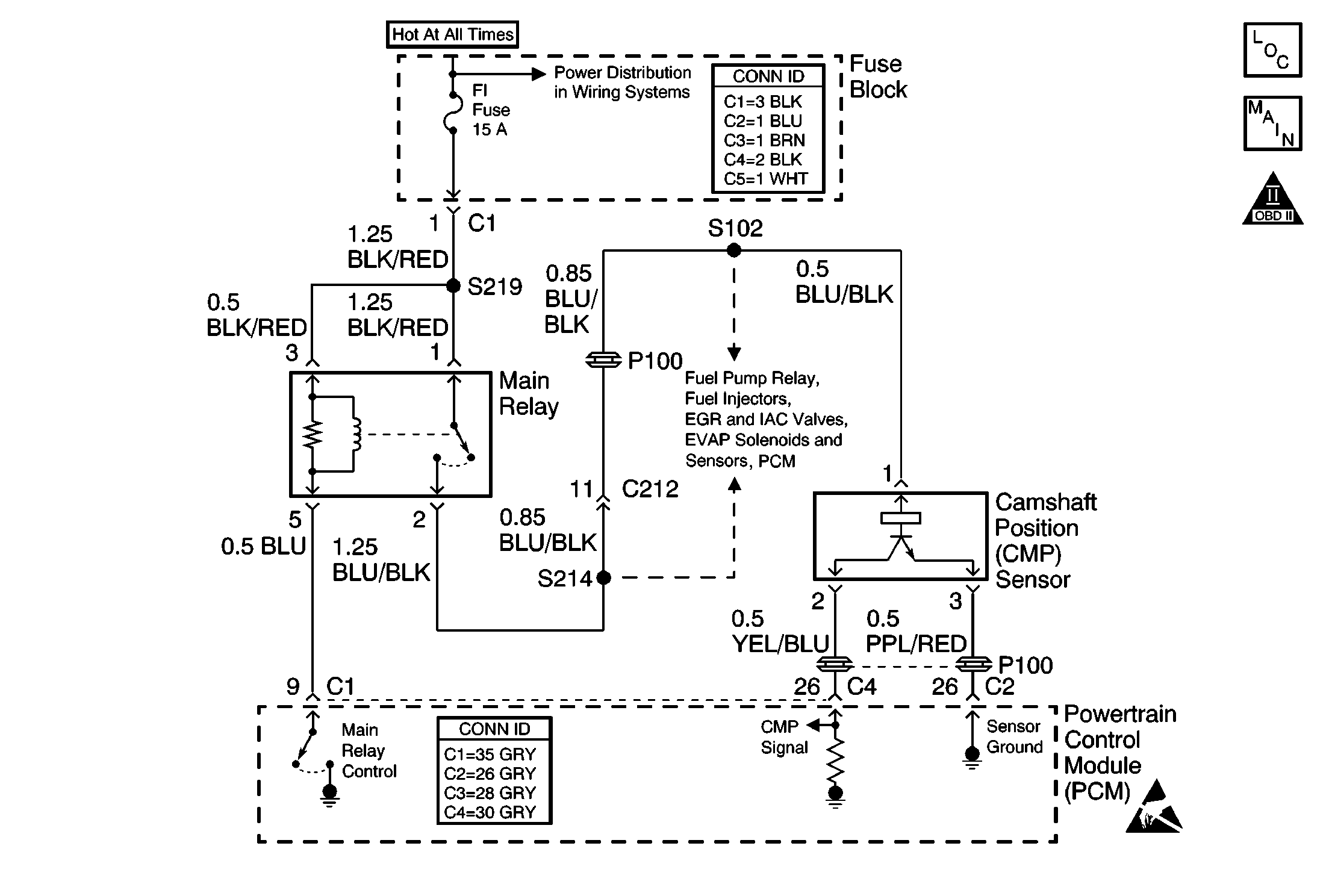
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is located at the rear of the cylinder head and consists of a signal generator (a hall element and magnet) and a signal rotor. As the signal rotor turns, a magnetic flux from the magnet is applied to the hall element repeatedly. The hall element generates a voltage that is proportional to the magnetic flux. The PCM uses this pulse/revolution signal in order to determine the engine speed and the position of each cylinder. The PCM uses this signal to control the fuel injectors and the ignition timing.
Condition for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is being cranked. |
| • | The engine is running. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No signal from the CMP sensor for 3 seconds with the PCM receiving an engine start signal.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive drive cycles without a fault present. |
| • | A DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The DTCs can be cleared by using a scan tool or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | If a DTC P1500 Starter Signal Circuit is set, diagnose P1500 first. |
| • | If no problem is found with the CMP sensor or the circuitry, check the CMP sensor signal rotor for proper alignment or damage. |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the CMP sensor circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating of terminals |
| • | Broken electrical connector locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals |
If the DTC P0340 is intermittent, driving the vehicle under the following conditions can verify whether the fault is present. Perform the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. Road test the vehicle while monitoring the DTC P0340 diagnostic on the scan tool under the Not Ran Since Code Cleared selection in the DTC Information menu. If a DTC P0340 appears in the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list, the P0340 diagnostic has not yet run. When the DTC P0340 does not appear in the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list, the P0340 diagnostic has run. If the MIL is NOT ILLUMINATED and there is no PENDING DTC Status in DTC Information, the P0340 diagnostic has passed. DTCs MUST BE CLEARED in order to view the CURRENT STATUS of the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list. DO NOT FORGET that the Not Ran Since Code Cleared list only indicates that the test has run, not whether the test passed or failed. The DTC Information screen must be checked for CURRENT or PENDING status, in order to determine the outcome of the diagnostic test involved.
If you cannot duplicate the DTC P0340, the information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining vehicle operating conditions since the DTC was first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain (OBD) System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and to store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step determines if a fault is present. Review the Freeze Frame data to determine when the DTC set. Always record this information.
-
A malfunctioning starter signal circuit (DTC P1500) can cause a false DTC P0340 to set.
-
This step checks for a mechanical malfunction. Inspect for a broken timing belt if the signal rotor does not turn.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate a DTC P0340? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
3 |
Is the voltage at the specified value? | B+ | ||||||||
4 | Probe the sensor connector terminal 3, harness side, with a test lamp connected to B+. Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
5 | Measure the voltage at the terminal 2 of the CMP sensor electrical connector, harness side, with a DMM. Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5 V | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | ||||||||||
7 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||
11 | Replace the CMP sensor. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
12 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
13 |
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | System OK |
