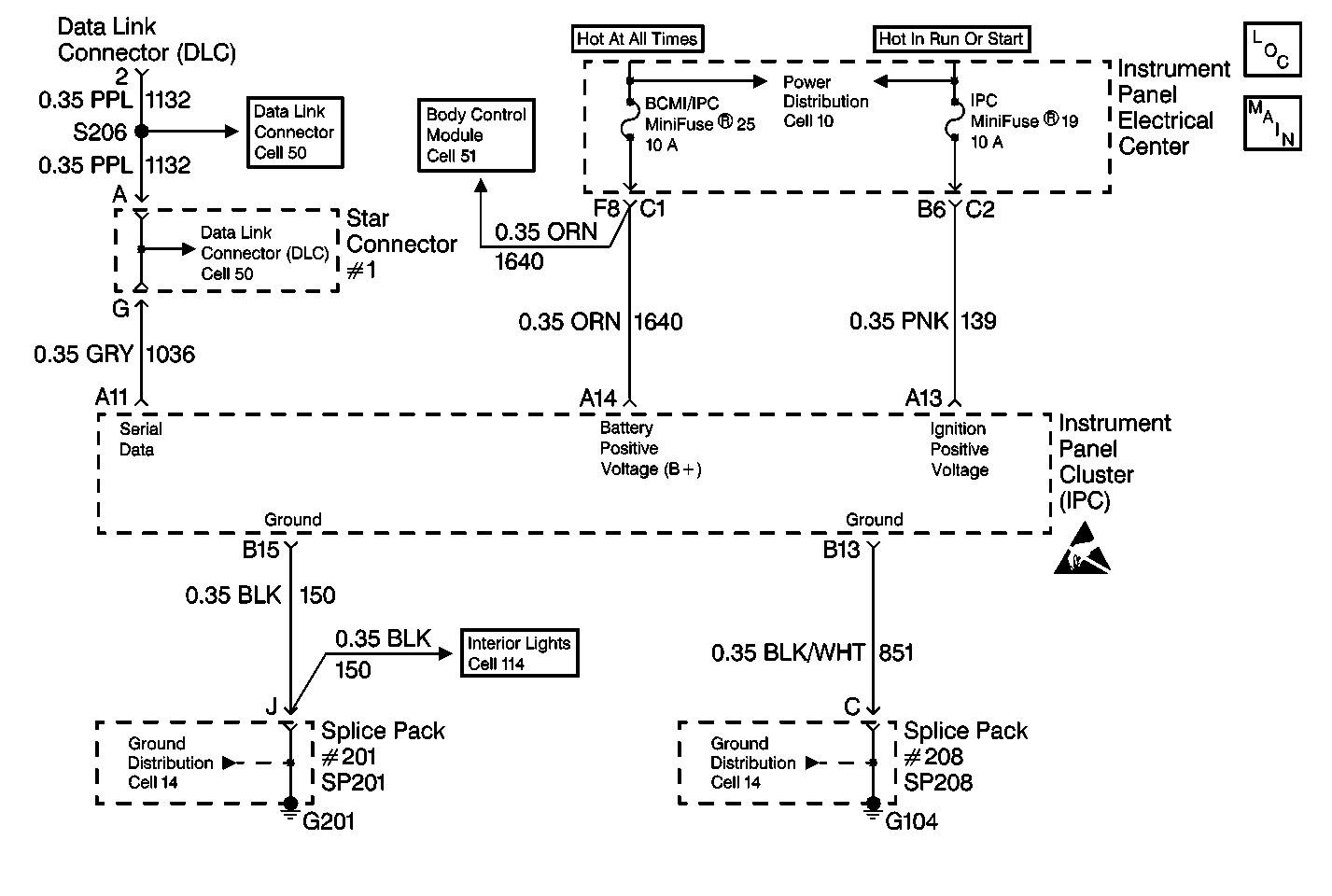
Circuit Description
The Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) Diagnostic System Check is an organized approach to identify problems associated with the IPC. This check must be the starting point for any IPC complaint, and will direct you to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. The IPC is a very reliable component and is not likely the cause of the malfunction. Most system complaints are linked to faulty wiring and connectors, and occasionally to components. Understanding the computer system and using the tables correctly will reduce diagnostic time and prevent unnecessary parts replacement.
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The following conditions may result in an intermittent operation of the IPC with no DTC stored: |
| - | Any condition which results in the interruption of power to the IPC |
| - | Out of range battery or ignition voltage |
Specification
Normal IPC operating voltage: 9.0-16.0 V
| - | A loose or damaged ground(s) |
| - | An open or shorted serial data line |
| • | An intermittent failure in the electronic system may be very difficult to detect and to accurately diagnose. The IPC test for different malfunctions under different vehicle conditions. For this reason, a thorough test drive is often needed in order to repeat a malfunction. If the system malfunction is not repeated during the test drive, a good description of the complaint may be very useful in locating an intermittent malfunction. Faulty electrical connections or wiring causes most intermitting problems. When an intermitting condition is suspected, check the suspected circuits for the following conditions: |
| - | Poor mating of connector halves or backed out terminals |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Wire chafing |
| - | Poor wire to terminal connections |
| - | Dirty or corroded terminals |
| - | Damage to connector bodies |
| • | If the IPC loses battery power with the ignition in the ON position, the IPC will display all "AAAAAAA" in the message display center. To prevent or clear this condition, disconnect the battery with the ignition in the OFF position. |
| • | If the IPC displays history communication DTCs (DTCs with the letter U as a prefix) , always clear these DTC first and check if they reset before preforming any diagnosis on the IPC. These communication DTC do not necessarily indicate an IPC malfunction, but may set under various conditions. |
| • | The IPC will display a combination of the following messages If the IPC cannot communicate properly on the serial data line: |
| - | SERVICE VEHICLE SOON |
| - | SERVICE TIRE MONITOR |
| - | ENGINE PROTECTED REDUCE ENGINE RPM |
| - | LOW FUEL |
| - | LOW TIRE PRESSURE |
| • | Use the J 35616 whenever a diagnostic procedure requests probing or checking a terminal. Using this adapter will ensure that no damage to the terminal will occur, and will give an idea of whether contact tension is sufficient. |
| • | If the DTC is a history DTC, the problem may be intermittent. Perform the tests shown while moving related wiring and connectors. This can often cause the malfunction to occur. Perform a thorough inspection of all related wiring and connectors pertaining to the history DTC stored. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections |
| • | Exit all scan tool tests before cycling the ignition OFF to ON unless the scan tool instructions direct otherwise. Follow the operating instructions in the scan tool operator's manual. Failure to follow these instruction may set DTCs, cause vehicle system malfunctions, set false DTCs, or cause scan tool malfunctions. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
This test determines if communications can be established with the IPC.
-
This test checks for stored IPC DTCs.
-
This test determines whether communications can be established with other systems connected to the same serial data line.
-
This test determines if any warning message are displayed on the IPC.
-
This test determines if the indicators are functioning properly.
-
This test checks for any open IPC power fuses.
-
This test checks the IPC power circuit. If the test light does not turn ON, there is an open in the IPC power circuit.
-
This test checks the IPC ground circuit. If the test light does not turn ON, there is an open in the IPC ground circuit.
-
This test determines if an open is present in the serial data line between the IPC and the DLC terminal 2 (CKT 1036).
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Does the scan tool communicate with the IPC? | -- | |||
Select display IPC DTC function with the scan tool. Are any DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC table | ||
Attempt to establish communications with the other systems connected to the same serial data line (PCM, RFA, BCM, etc.). Does the scan tool communicate with the other systems? | -- | |||
Check for any warning messages displayed on the IPC. Refer to Warning/Status Message List . Are any warning messages displayed? | -- | |||
Check for proper indicator operation. Refer to Indicator Lamps . Do all the indicator operate correctly? | -- | System OK | Go to the Applicable Indicator Diagnostic table | |
Does the test light turn ON in all circuits? | -- | |||
Does the test light turn ON in all circuits? | -- | |||
With a test light connected to B+, probe all IPC ground circuits. Refer to Instrument Cluster: Analog Schematics . Does the test light turn ON in all circuits? | -- | |||
Check for continuity between the IPC connector terminal (harness side) A11 and DLC terminal 2. Is there continuity? | -- | |||
10 | Replace the IPC. Refer to Instrument Cluster Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Repair the open in the ignition feed to IPC fuse. If the fuse is open, locate and repair the short to ground in the circuit connected to the open fuse. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Locate and repair the open in CKT 1036. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Locate and repair the open in the IPC power circuit. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Locate and repair the open in the IPC ground circuit. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
15 |
Are all DTCs cleared? | -- | System OK | -- |
