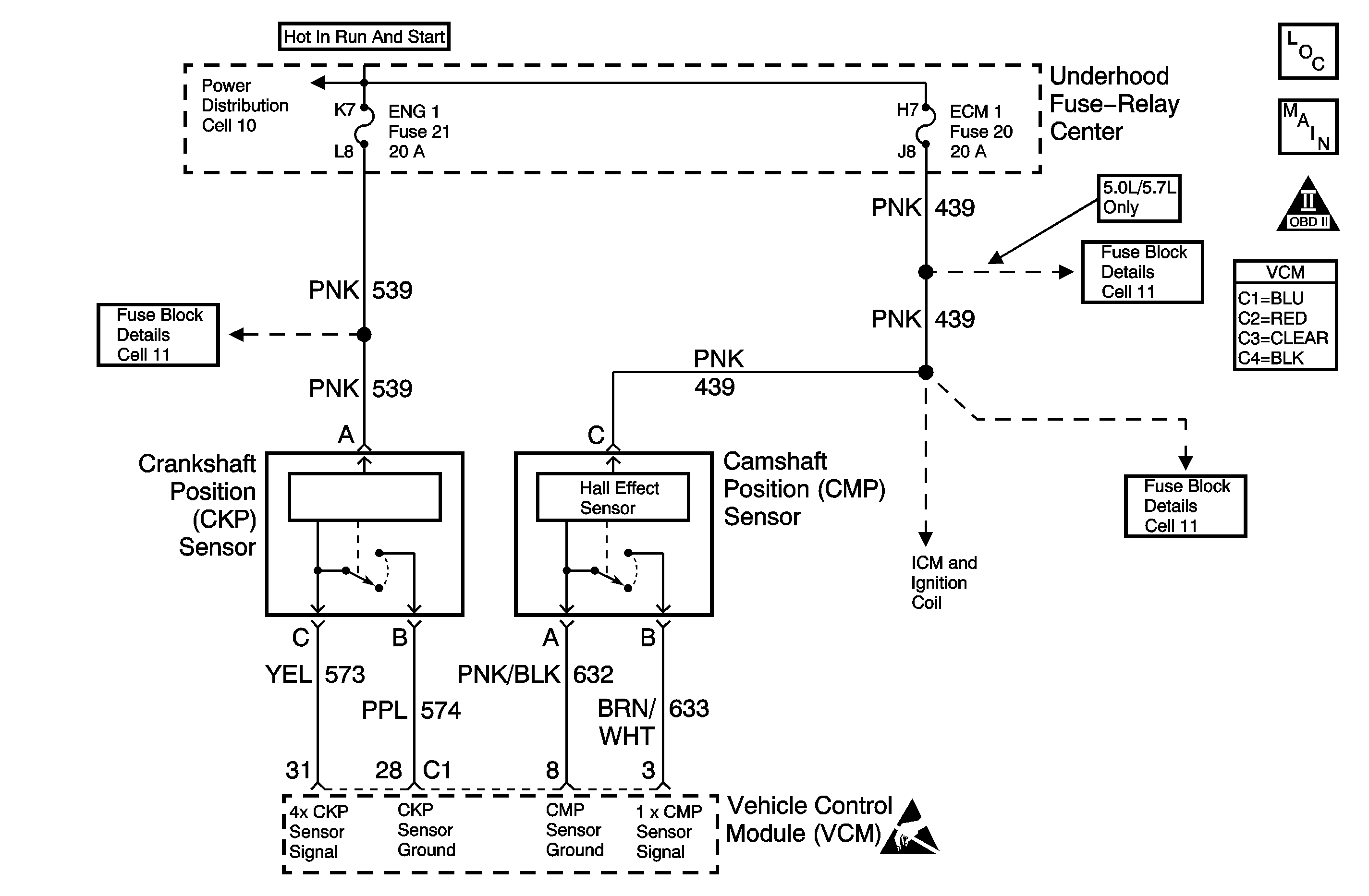
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is a sensor designed to detect changes in a magnetic field. The control module supplies the CKP sensor a signal and ground circuits. Ignition voltage is supplied to the sensor by an independent circuit. The CKP sensor produces a magnetic field whenever the ignition is ON. The CKP sensor is mounted near a reluctor wheel that is attached to the crankshaft. When the crankshaft rotates, when the engine is cranking or running, the toothed reluctor wheel changes the magnetic field. The CKP sensor converts each change in the magnetic field into a PULSE. The number of teeth on the reluctor wheel determines how many pulses the CKP sensor detects per crankshaft rotation. The CKP sensor signal is used in order to determine the engine speed, the crankshaft position, and to detect misfire.
If the CKP frequency is more than expected by the VCM, this DTC will be set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine speed is less than 4,000 RPM |
| • | The MAF is 5 g/s or more |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The CKP sensor duty cycle is more than a calibrated value
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module stores the DTC in history after the first failure but will not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. |
| • | A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 70°C (160°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the face of the CKP sensor for metal shavings. This could result in an intermittent DTC.
Also check for the following conditions:
| • | A chipped or damaged reluctor wheel |
| • | Incorrect reluctor wheel |
| • | Incorrect alignment of the CKP sensor to reluctor wheel |
| • | Excessive crankshaft end play |
Refer to Symptoms
Check for Electro-magnetic Interference.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step determines if DTC P0338 is the result of a hard failure or an intermittent condition.
-
This test checks the crank sensor for too high of a duty cycle.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the engine start? | -- | |||
Does DTC P0338 set? | -- | |||
Important: The red (positive) lead from the DMM must be connected to the CKP (4X) signal circuit. Is the duty cycle more than the specified value? | 43 % | |||
5 | Check the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the reluctor wheel for damage. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
6 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 |
Important: Inspect the CKP sensor mounting surface in order to insure the surface is clean and free of debris.
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
9 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
11 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
